Explain Why the Difference Between Engineering Strain and True Strain
Yet it should be noted that the true stress could be much larger than the engineering stress once the strain increases and the consequently the cross sectional of the specimen decreases. In the z 0 plane where the analysis is performed w is zero.

Is There Any Difference Between The True Strain And Elastic Strain Under The Elastic Region Ansys Learning Forum
22 and 27 on p.
. Stress while the true strain is smaller than the Engg. Sile and compressive strains. 0 0 l l l e True strain ln ln1 0 0 0 A A l l dl l l l This is.
Create a material Calibration. Hookes law explains the relationship between stress and strain. Engineering strain is the amount that a material deforms per unit length in a tensile test.
True strain equals the natural log of the quotient of current length over the original length. In both cases of tension and compression the difference increases as strain increases. Also known as nominal strain.
This is true for both tensile and compressive strains. The difference between the engineering and true strains becomes larger because of the way the strains are defined respectively as can be seen by inspecting Eqs. For a given value of the load and elongation the true stress is higher than the Engg.
Engineering Stress-Strain Curve vs. This is true for both tensile and compressive strains. At any load the engineering stress is the load divided by this initial cross-sectional area.
Explain ENGINEERING STRESS assumes that the area a force is acting upon remains constant. This is true for both tensile and com pressive strains. TRUE STRESS takes into account the variation in the cross sectional area as a result of the stress induced deformation of a material.
30 and 29 on p. Hi True stress is obtained by dividing the test load by the instantaneous varying true area whereas the engineeing stress is the result of. At any load the true stress is the load divided by the cross-sectional area at that instant.
The answer lies in the fact that the definitions of engineering strain and true strain are different the latter being based on the actual or instantaneous dimensions as can be seen in Eqs. Without getting into all the math the engineering strain utilizes the initial length of the specimen in the calculation the true strain utilizes the instantaneous length of the specimen. Thus there are still only two components of the displacement field u and v to be solved forThere are however three new unknowns a b and cIn a common interpretation of generalized plane strain only the coefficient c is used.
Is this phenomenon true for both tensile and compressive strains. The difference between the engineering and true strains becomes larger because of the way the strains are defined respectively as can be seen by inspecting Engineering strain or normal strain. Unless thickness and width are being monitored continuously during the test you cannot calculate true stress.
According to Hookes law the strain in a solid is proportional to the applied stress and this should be within the elastic limit of that solid. Also known as nominal strain. The relationship between the true.
30 and 29 on. Conversely since true strain is calculated by integrating the strain over the entire test it is larger than engineering strain for the same value of displacement. The difference between the engineering and true strains becomes larger because of the way the strains are defined.
Explain why the difference between engineering strain and. The difference between the engineering and true strains becomes larger because of the way the strains are defined respectively as can be seen by inspecting Eqs. The analytical equations for converting engineering stress-strain to true stress-strain are given below.
In Abaqus the following actions are required for converting engineering data to true data given that the engineering stress-strain data is provided as a txt file. Relation between True and Engineering Stress-Strain. Explain why the difference between engineering strain and true strain becomes larger as strain increases.
A True Stress True Strain Curve. Engineering strain is the amount that a material deforms per unit length in a tensile test. Physically this means that the long object is allowed to expand axially in.
While you are pulling the length increases but the width and thickness shrink. True strain equals the natural log of the quotient of current length over the original length as given by Eq4. 24 Using the same scale for stress we note that the tensile true-stress-true-strain.
The relation between stress and strain is that they are directly proportional to each other up to an elastic limit.
Engineering Stress Strain Vs True Stress Strain Ahss Guidelines
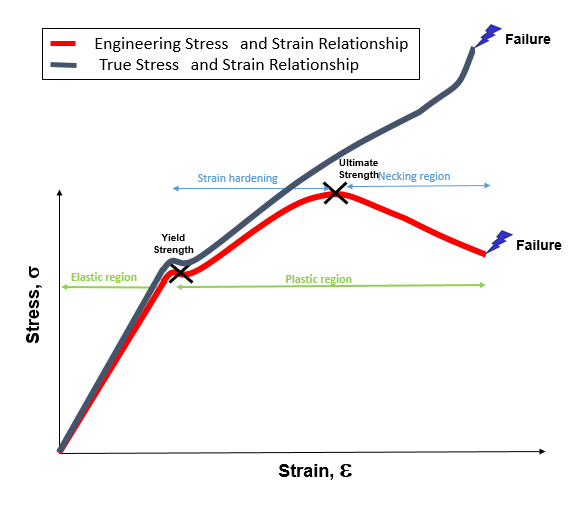
Engineering Stress Strain Vs True Stress Strain Yasin Capar

Difference Between Engineering Stress And True Stress Youtube
Engarc L True Stress True Strain Engineering Stress And Engineerin Strain
No comments for "Explain Why the Difference Between Engineering Strain and True Strain"
Post a Comment